- info@ficci.org.bd
- |
- +880248814801, +880248814802
- Contact Us
- |
- Become a Member
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |

Agribusiness: The fundamental to sustain the human civilization
Agriculture, food security, and agribusiness play a vital role in ensuring the well-being of societies and economies worldwide. "According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, around 690 million people globally suffer from hunger, while 3 billion people cannot afford a healthy diet."
These alarming statistics highlight the urgent need to address food security challenges. Agribusiness, which encom- passes the entire value chain from production to processing and distribution, is a key driver in achieving food security. It not only provides sustenance but also contributes significantly to employment, income generation, and economic growth. In fact, "the FAO estimates that agriculture and agribusiness account for around 10% of global GDP"
How innovations can save Agribusiness and the Planet:
Innovative approaches in agribusiness have become crucial in addressing the challenges faced by the global agricultural sector. According to the United Nations (UN), the world population is projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, which will require a significant increase in food production. However, this task is further complicated by factors such as climate change, limited resources, and the need for sustainable practices.
To tackle these challenges, various innovative approaches have emerged in agribusiness. One such approach is precision agriculture, which utilizes advanced technologies like remote sensing, drones, and GPS to optimize farming practices. Precision agriculture enables farmers to monitor and manage their crops more efficiently, resulting in increased yields and reduced resource wastage. According to the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), precision agriculture can potentially increase crop yields by up to 20% while reducing water usage by 30%.

Another innovative approach is vertical farming, which involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often in urban environments. This method utilizes hydroponics or aeroponics systems, where plants are grown without soil and receive nutrients through water or mist. Vertical farming offers several advantages, including year-round production, reduced land usage, and minimal water consumption. The UN estimates that vertical farming can produce up to 20 times more crops per square meter compared to traditional farming methods.
Furthermore, agribusiness is increasingly embracing digital technologies and data-driven solutions. The use of big data analytics, artificial intelligence, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices enables farmers to make informed decisions regarding crop management, pest control, and resource allocation. These technologies provide real-time data on weather conditions, soil moisture levels, and crop health, allowing farmers to optimize their operations and minimize risks. The UN reports that digital agriculture can potentially increase smallholder farmers' incomes by up to 60%. In addition to these technological advancements, agribusiness is also focusing on sustainable practices to ensure long-term food security. The UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) emphasize the importance of sustainable agriculture, including the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, preservation of biodiversity, and promotion of responsible land use. Innovative approaches such as agroforestry, organic farming, and regenerative agriculture are gaining traction as they offer environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional farming practices.

Agribusiness: Bangladesh Context
Bangladesh is an agrarian country with a tropical climate perfectly suited for the production of a variety of crops, fruits, vegetables, livestock, and fisheries, as well as a promising agro and food-processing industry. The agriculture sector employs 38 percent of the workforce and contributes to 14 percent of the country's Gross Domestic Product (GDP). The growth rate of this sector accounts for 3.2 percent.
National strategies have identified the agriculture sector as a high priority and have a targeted focus on developing agribusiness in the country. The agribusiness sector offers numerous opportunities both globally and in the local market. To realize these opportunities, global multinational food companies like Nestlé can support the overall agribusiness sector by imparting technical knowledge and providing support on good agricultural practices, which are prerequisites for sourcing for global brands. This support can help integrate Bangladesh into global agribusiness supply chains.
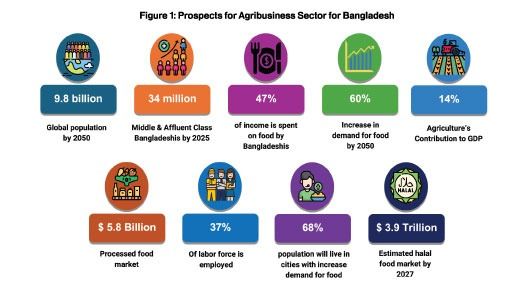
Globally, the demand for food is projected to rise by 60 percent by 2025. It is estimated that 68 percent of the popula- tion will live in cities by 2050 with increased demand for processed goods. By 2025, the halal food market is estimated to reach $3.9 trillion. In the context of Bangladesh, 34 million people are estimated to be in the Middle and Affluent (MAC) category by 2025 which will inherently increase demand for food. The market for processed food in Bangladesh is expected to reach $5.8 billion by 2030. Evidence reveals that on average, Bangladeshis spend 47 percent of their income on food and considering the size of Bangladesh's population, this makes the country a huge domestic market for agribusiness/food products.
Key challenges that are constraining agribusiness competitiveness in Bangladesh:
Agribusiness in Bangladesh faces several key challenges that hinder its prospects for growth and development. These challenges include:
1. Increased pressure on arable land: Bangladesh has a high population density, resulting in limited availability of arable land. The growing population and urbanization further exacerbate the pressure on land, making it difficult for farmers to expand their agricultural activities and increase productivity.
2. Unfair prices: Farmers often face challenges in obtaining fair prices for their produce. Middlemen and intermediaries in the supply chain often exploit farmers, offering low prices for their crops while selling them at higher rates in the market. This unfair pricing system leaves farmers with limited profits and discourages them from investing in their agribusiness.
3. Inadequate access to knowledge, technology, and other resources: Many farmers in Bangladesh lack access to modern agricultural practices, knowledge, and technologies. Limited access to information on improved farming techniques, crop varieties, and pest management hampers their productivity. Additionally, inadequate access to credit, irrigation facilities, and quality seeds further restricts their ability to enhance their agribusiness.
4. Lack of investments in infrastructure, capability, and capacity development: Insufficient investments in rural infrastructure, such as roads, storage facilities, and irrigation systems, hinder the growth of agribusiness. Additionally, there is a lack of focus on developing the capabilities and capacities of farmers through training programs, workshops, and skill development initiatives.
5. Lack of incentivization of the sector: Agribusiness in Bangladesh often lacks adequate incentives and support from the government. Limited subsidies, tax breaks, and financial assistance for farmers and agribusiness enterprises discourage investment and innovation in the sector.
6. Lack of intervention in improving livelihoods of farmers: The livelihoods of farmers in Bangladesh are often vulnerable to various risks, including natural disasters, market fluctuations, and climate change impacts. There is a need for effective interventions and policies that address these challenges and provide social protection to farmers, ensuring their sustainable livelihoods.
7. Improper utilization of cultivated crops for processed food: Bangladesh has a significant potential for agro-processing industries, but there is a lack of proper utilization of cultivated crops for value-added products. Insufficient investment in processing facilities and limited market linkages result in a significant portion of crops going to waste or being sold at lower prices.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that includes policy reforms, investments in infrastructure and technology, capacity building programs, and market interventions. By addressing these constraints, Bangladesh can unlock the full potential of its agribusiness sector, improve farmers' livelihoods, and contribute to food security and economic growth.
What is needed to increase competitiveness in Agribusiness sector of Bangladesh:
To increase competitiveness in the agribusiness sector in Bangladesh, several types of support are needed. Firstly, there is a need for investment in infrastructure development. This includes improving rural roads, irrigation systems, and storage facilities. According to the World Bank, inadequate infrastructure is one of the major constraints faced by agribusinesses in Bangladesh, leading to post-harvest losses and higher transportation costs. By investing in infrastructure, agribusinesses can enhance their efficiency, reduce wastage, and improve market access, ultimately increasing their competitiveness.
Secondly, agribusinesses in Bangladesh require access to finance and credit facilities. Lack of access to affordable credit is a significant challenge faced by small and medium-sized agribusiness enterprises. According to the Bangla- desh Bank, only around 10% of agricultural loans are provided to small and medium-sized enterprises. Access to finance is crucial for agribusinesses to invest in modern technologies, purchase quality inputs, and expand their operations. By ensuring easier access to finance and credit, agribusinesses can enhance their productivity, adopt innovative practices, and compete effectively in the market.
How Nestlé can Contribute to Develop Processed Food Industry in Bangladesh to uplift the Agribusiness sector by reduce Import Dependency and Open Window for Scaling Up Export
Nestlé can help the agriculture and agribusiness sector in Bangladesh in several ways.
Firstly, Nestlé can provide the technical know-how and knowledge on Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) to farmers and relevant authorities and how products can meet global standards. Moreover, once the products are produced in accordance with the best global standards, it can also be exported. Similarly, following global standards will enhance the quality of local products in terms of nutrition and safety.

In conclusion, innovative approaches in agribusiness are crucial for bridging tradition and technology in Bangladesh's agricultural sector. Precision agriculture, vertical farming, digital technologies, and sustainable practices can address challenges and improve competitiveness. Investment in infrastructure and access to finance are needed to support agribusiness growth. Global multinational food companies like Nestlé can contribute by providing technical knowledge, supporting good agricultural practices, and connecting local products to global supply chains. By embracing innovation and receiving support, Bangladesh's agribusiness sector can thrive, ensuring food security and economic growth.
In summary, innovative approaches and support are essential for the competitiveness of agribusiness in Bangladesh. Investment in infrastructure and access to finance are needed, while global multinational companies like Nestlé can provide technical knowledge and connect local products to global markets. By embracing innovation, Bangladesh's agribusiness sector can flourish, ensuring food security and economic prosperity.





