- info@ficci.org.bd
- |
- +880248814801, +880248814802
- Contact Us
- |
- Become a Member
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |

The way Bangladesh has managed its economic recovery during this pandemic is better than the comparable economies. As per the GDP forecasts for FY 2022-2023, Bangladesh will be one of the faster growing nations in the near future. However, tax GDP ratio is still lowest in the region and tax collections might not increase as proportion to growth of economy when the SEZ becomes fully operational coupled alongside the fear of new Covid variants and geopolitical tensions which have already increased cost to the business. I would like to put forward some specific proposals keeping in mind the forthcoming budget for 2022-2023.
A. Rationalization of TDS rate
Last year, the Government reduced the company tax rate from 32.5% to 30%. Corporates have been claiming for a long time that Bangladesh's tax rate is significantly higher than its neighbors and competitors. Corporates demanded a further decrease in the tax rate this year as well. Higher tax rates create a reluctance on the part of corporates to pay taxes, which is considered to be one of the reasons for lower tax-GDP rates.
I would like to thank the Prime Minister and the Finance Minister for their courage in reducing the corporate tax rate from 35% to 30% in the last two years. There is a growing demand to reduce it further to 25%. But in reality, will the tax burden of corporates be reduced if the tax rate is reduced? Will Bangladeshi businessmen be able to compete with neighboring and competing countries?
At per latest annual report (AY 2019-2020) of NBR, almost 60% (41,804 cr) income tax is being collected by way of tax collection/deduction at source. Out of this, approximately 60% tax is collected under section 52, 53 and 53F.The importer has to pay 5% income tax at the time of importing the goods, i.e., if the importer of the goods sells it ready-made and if the net profit is more than 16.67%, then he can adjust the tax paid at the source. In addition, if the company imports raw materials, manufactures finished goods and supplies, its customer will maximum 7% tax from the source as per section 52, which is the minimum tax as per section 82 (c). In order to adjust the tax deduction, the company has to earn a further 23.33% net profit. In reality, most companies could not make such a profit under normal circumstances, and it is impossible in the case of Covid 19.
An example will perhaps better illustrate the scenario:
 Suppose a company imported raw material worth BDT 30 crore in a year. At the time of import, the company had to pay 5% import tax amounting to Tk 1.5 crore. These products are manufactured and sold to its customers for BDT 50 crore. Out of this sale, Tk. 20 crore is sold to corporate customers whose taxes are deducted at the source. Under the earlier provision, another Tk. 1 crore is deducted at source and according to the current provision, Tk. 1.4 crore will be deducted at source. The remaining BDT 30 crore worth of products are sold normally. So, if the tax rate for such traders is reduced from 32.5% to 30%, will the tax burden of corporates be reduced?
Suppose a company imported raw material worth BDT 30 crore in a year. At the time of import, the company had to pay 5% import tax amounting to Tk 1.5 crore. These products are manufactured and sold to its customers for BDT 50 crore. Out of this sale, Tk. 20 crore is sold to corporate customers whose taxes are deducted at the source. Under the earlier provision, another Tk. 1 crore is deducted at source and according to the current provision, Tk. 1.4 crore will be deducted at source. The remaining BDT 30 crore worth of products are sold normally. So, if the tax rate for such traders is reduced from 32.5% to 30%, will the tax burden of corporates be reduced?
It is evident from the table above that in the case of such corporates, if the sales and profits remain unchanged, their tax will not be reduced but the effective tax rate will be increased from 50% to 58% because of increase in the rate of withholding tax. The reverse tax burden is increasing due to unchanged source tax collection at the import stage and increase in the source tax rate at the supply stage.
Hence, it is very important for the Government to reduce the tax collection at source to at least 3% from 5%. Recently there is a significant growth observed in terms of import of goods. There is also an upward trend of devaluation of USD. Hence, overall collection from import is unlikely to fall even if the tax at source is reduced. This will give a big relief to the local manufacturer.
Construction company
 Suppose a company does construction work worth BDT 100 crore a year. The cost of that company is BDT 75 crore per year. According to the earlier provision, a withholding entity deducts Tk 5 crore from the source and according to the current, Tk 7 crore will be deducted from the source. So, if the tax rate for such construction company is reduced from 32.5% to 30%, will the company’s tax be reduced? Let us have a look.
Suppose a company does construction work worth BDT 100 crore a year. The cost of that company is BDT 75 crore per year. According to the earlier provision, a withholding entity deducts Tk 5 crore from the source and according to the current, Tk 7 crore will be deducted from the source. So, if the tax rate for such construction company is reduced from 32.5% to 30%, will the company’s tax be reduced? Let us have a look.
It is evident from the table above that in the case of a service provider, even if their revenue and profits remain unchanged, their tax burden will not be reduced but will remain unchanged even though the proposed tax rate reduction should have reduced their tax burden.
Currently, DVS (Document Verification Systems) has been introduced through joint initiative by NBR and ICAB. The tax authorities can easily identify the profitability of the industry by analyzing the income and profit before tax information available in DVS.
Therefore, if the rate of collection and deduction at source, especially in sections 52, 52AA, 53 of the Income Tax Ordinance, 1984, is not reduced, the corporate tax rate will not be reduced, and the tax burden of corporates will not be reduced.
Are we still comparable?
Although the current corporate tax rate has been reduced, let us see what the difference is with neighboring and competing countries :
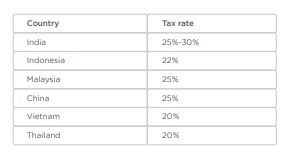 The table above shows that our tax rates are still high which reduces the net income of the companies and leaves them behind in the competition. Increasing income will increase investment which will create new employment in Bangladesh and will assist in generating revenue. Reducing tax rates will encourage companies and increase transparency in financial statements. As a result, it will help increase the revenue collection of Bangladesh. Many people think that reducing the tax rate will reduce the revenue collection. However, it can be seen that in the tax year 2013-14 to 2014-15, the tax rate was reduced from 37.5% to 35% but the revenue collection increased from Tk 125,000 crore to Tk 135,028 crore. Although the tax rate was reduced from 35% to 32.5% last year due to the prevalence of corona, the revenue collection has increased by 12.87% from July 2020 to April 2021.
The table above shows that our tax rates are still high which reduces the net income of the companies and leaves them behind in the competition. Increasing income will increase investment which will create new employment in Bangladesh and will assist in generating revenue. Reducing tax rates will encourage companies and increase transparency in financial statements. As a result, it will help increase the revenue collection of Bangladesh. Many people think that reducing the tax rate will reduce the revenue collection. However, it can be seen that in the tax year 2013-14 to 2014-15, the tax rate was reduced from 37.5% to 35% but the revenue collection increased from Tk 125,000 crore to Tk 135,028 crore. Although the tax rate was reduced from 35% to 32.5% last year due to the prevalence of corona, the revenue collection has increased by 12.87% from July 2020 to April 2021.
B. Some sections need to be gradually withdrawn from section 82C
Currently tax deducted or collected at source under section 52, 52AA, 53, 53E is considered as minimum tax. Income tax is a tax leviable only on the income of a taxable entity not on the sale or receipt of a transaction.A corporate taxpayer is required to keep accounting and compliance in accordance with the International Financial Reporting Standards. Audited financial statements are verified through DVC. A corporate taxpayer is required to submit a single audited financial statement to the lending banks, NBR, RJSC, the Securities Exchange Commission, the Financial Reporting Council. Hence, reliability on audited financial statement will increase. As such it is recommended to exclude the deductions / taxes levied at the source under Section 52, 52AA, 53, 53E from minimum tax u/s 82c.
C. Treatment of disallowances (Over burden of tax)
As per current provision under section 30B, the amount of disallowances under section 30 shall be treated separately as “Income from business or profession” and tax will be payable thereon at the regular rate.The introduction of section 30B in the Income Tax Ordinance 1984 is not consistent with the principles of the Income Tax Act. Under this section, a company has to pay tax at regular rate on those expenses if there is any unauthorized expenditure under section 30, even if the company incurs loss. Section 30 of the Income Tax Ordinance applies to unapproved expenses. But there are some provisions under section 30 under which companies voluntarily pay taxes, such as:
• Excess perquisite u/s 30 (e),
• Royalty, technical fees u/s 30 (h)
, • Incentive bonus u/s 30 (j) and
• Foreign travelling u/s 30 (k).
It is, therefore, more reasonable to apply the provisions of section 30B, only for non-compliance under section 30 for matters relating to:
• Non deduction of tax at source
• Not obtaining ETIN
• Non-payment through banking channel
D. Increase Tax net
We have recently witnessed the benefit of integration between BRTA and NBR. Now undisclosed vehicle can be traced with the ETIN. Specific proposals for increasing the tax net are as follows:
• Integration of NBR server with Land records office server to run and reconciliation of both of the servers on yearly basis. This will confirm the disclosure of land assets to the tax file the assessee.While processing the tax return it will automatically generate exception report to the assessing officer if an assessee does not report the buy/sell of property in their tax return. Section 184 (3) (vii) requires submission of TIN for registration of land, building or apartment. Many do not disclose land purchase / sale information in their tax files. As there is no link between the Land Records Office and the NBR, the tax authorities are unable to identify such transactions and the scope for undisclosed assets remain. If the amount / account of undisclosed land can be calculated by coordinating with the server of the Land Records Office and the income tax return filed with the NBR, then the amount of tax payable on undisclosed income and income can be determined. This will increase the revenue of the Government and reduce the number of undisclosed lands in future.In this case MOU with NBR and LGRD Ministry will be able to prevent tax evasion by checking the taxpayer's return through the tax inspector with the account of land / property registration against TIN.
• It is also recommended to insert in section 184A of the ITO, 1984 that submission of ETIN mandatory at the time of filing holding tax returns. This will confirm the disclosure of assets to the tax file the assessee. Those who have land or building in City Corporation area are required to pay holding / municipality tax. There is a tendency that an assessee pays holding tax to City Corporation but do not disclose the asset in the income tax return despite having property in the area and the Government is deprived of the due revenue. It is presumed to have taxable income if you have property in City Corporation area. Therefore, it should be made compulsory for the person who is paying holding tax to submit TIN. NBR may collect the information centrally and circulate zone-wise record so that the same can be reconciled with the tax return submitted by the assessee.
E. Increasing number of return filing
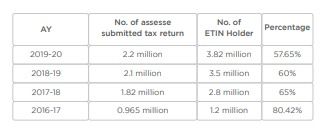 As per the news published in the newspaper approximately 42% ETIN holder submitted their tax return for the assessment year 2020-2021 and the percentage is declining on year by year although return submission has been made mandatory from AY 2020-2021.
As per the news published in the newspaper approximately 42% ETIN holder submitted their tax return for the assessment year 2020-2021 and the percentage is declining on year by year although return submission has been made mandatory from AY 2020-2021.
Those data revealed to us that no. of assessee submitted tax return has declined based on the no. of TIN holder. A question may come why such trend was happened. The underlying reason for such deviation is that through Finance Act 2017, NBR inserted a new section 184A where NBR accommodated a provision that in certain cases it is mandatory to show proof of TIN Certificates to get the services as mentioned in section 184A. After insertion of this section many individuals and corporate houses collected TIN Certificate to avail those services hence the number of TIN holder was increased substantially in that year.
NBR will remind/inform ETIN holder to submit their return over cell phone (by messaging/calling). Mobile numbers of all non-filers need to be collected centrally and can be used for sending SMS and subsequent follow up through the concerned circle. NBR can also outsource the communication to a call center. In extreme cases NBR may request BTRC to cancel SIM cards and not to issue new SIM cards to non-filers.
These activities will help increase the rate of return submission. Currently, many taxpayers do not file income tax returns even after taking TIN. Many taxpayers will be tempted to file returns if the NBR provides notification to the taxpayers through text messages or emails from time to time. Taxpayers are now asked to file VAT returns with future penalties through regular messages or emails from the VAT circle. In this way the taxpayers are informed about the return submission and submit the return. If the NBR informs the taxpayer through various communication with the mobile number from the taxpayer's database, the amount of return submission will increase.
Currently Bangladesh Investment Development Authority (BIDA) requires a company to file tax clearance certificate of the company while issuing/renewing work permit of expatriates. However, all companies are not required to be registered with BIDA and all companies do not employ foreign national.
(i) chambers not to renew membership of a member failing to file copy of the acknowledgment receipt of tax return.
(ii) require the professional bodies not to renew the practicing license to the professional accountants, doctors, engineers if they fail to submit proof of tax return filing.
F. Digitization of legal activities
Although the Income Tax Ordinance, 1984 introduced electronic filing for returns as a step towards digitization, the present Income Tax Ordinance, 1984 does not provide for any method of hearing, appeal, and tax assessment through electronic means. Online hearings have been introduced during the covid epidemic in the High Court and elsewhere. This system has been introduced in the neighboring country, India. The introduction of electronic means of appeal and hearing will reduce the embarrassment of both the taxpayer and the revenue officer.
Written by Snehasish Barua, FCA, ACA (ICAEW),
Partner, Snehasish Mahmud & CO. (SMAC)





